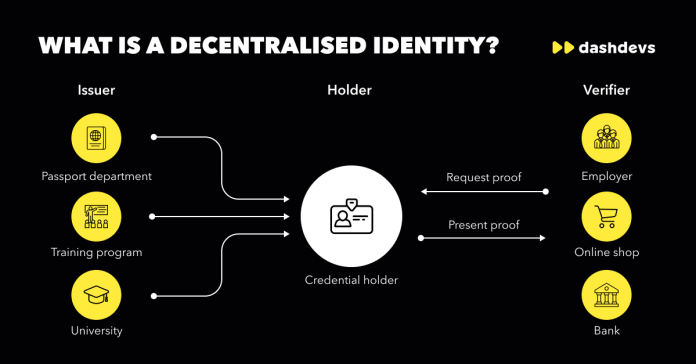
Decentralised identity is a rising trend that holds the potential to revolutionise how we verify identity and safeguard personal information in the age of technology. With the rise of data breaches and privacy infringements, the significance of ensuring secure identity verification cannot be emphasised enough.
Blockchain and Decentralized Identity
The advent of blockchain technology is transforming our understanding and administration of digital identity, paving the way for a decentralised identity system. Utilising a secure and distributed structure, blockchain has laid the foundation for a novel strategy in handling digital identities. This innovative approach promotes individual empowerment, ensures security, and respects privacy.
Core Components
At the core of blockchain-driven decentralised identity are three fundamental components: Decentralised Public Key Infrastructure (DPKI), Distributed Storage, and Administration and Oversight.
Instead of traditional centralised bodies handling cryptographic key oversight, Decentralized Public Key Infrastructure (DPKI) steps in. Instead, it disseminates the responsibility of maintaining and validating these keys across the blockchain network. This decentralised approach ensures that no single entity can compromise the security of the entire system, thereby making it resilient against a broad array of attacks.
Decentralised Storage is another pillar of decentralised identity systems. Traditional digital identity management systems store user data in centralised servers, creating attractive targets for hackers and raising concerns about data privacy. In contrast, decentralised storage disperses encrypted fragments of user data across the blockchain network. This approach guarantees that even if a part of the network falls into the wrong hands, the attacker cannot decipher meaningful information from the fragmented data.
Manageability and Control is about enabling individuals to control their digital identities. In decentralised identity systems, individuals possess full authority over their personal information, enabling them to determine the specifics of data sharing, such as the manner, timing, and recipients involved. This user-centric approach to data management significantly enhances privacy and security.
On Bitcoin
The Bitcoin blockchain is particularly relevant to decentralised identity due to its unique features. Bitcoin boasts superior scalability, making it capable of handling a large volume of transactions and data. This feature is crucial for deploying decentralised identity solutions, which need to manage countless identity transactions and a vast amount of associated data. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s security, transparency, and immutability are vital to maintaining trust in decentralised identity systems. The Bitcoin blockchain can effectively support the core components of decentralised identity—DPKI, decentralised storage, and manageability and control—thereby providing a robust infrastructure for secure and private identity verification.
Decentralised Identity vs Centralised Identity
Decentralised identity systems offer significant advantages over their centralised counterparts. While centralised systems are susceptible to single-point failures and potential misuse of authority, decentralised identities empower individuals by returning control of their personal data back into their hands. This setup ensures that data is only shared with consent, thereby improving data security and privacy.
Self-Sovereign Identity
Central to the concept of decentralised identity lies the idea of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). SSI empowers individuals with complete authority over the administration and governance of their digital personas. The framework of SSI rests on three pillars:
- Blockchain: The immutable and transparent nature of blockchain guarantees the authenticity of the identities.
- Verifiable Credentials (VCs): These are digital attestations of the identity attributes, offering privacy-preserving verification.
- Decentralised Identifiers (DIDs): These unique identifiers ensure each entity can be securely and independently verified.
- The role of digital wallets is also crucial in managing SSIs, allowing individuals to store and manage their identity credentials securely.
Pros and Cons of Decentralised Identity
Decentralised identity carries significant benefits, including enhanced control over personal data, superior security through cryptography, improved privacy, and simplified user experiences. However, it also presents several challenges, including difficulties in adoption, regulatory hurdles, and interoperability issues. The industry needs to address these challenges to realise the full potential of decentralised identities.
Decentralised Identity Protocols
Several decentralised identity protocols have emerged to help standardise and facilitate the adoption of this revolutionary technology. These include MetaID, uPort, 3Box, Veramo, Serto, ION, Dock, Sovrin Network, ORE ID, and Humanode. Each of these platforms offers unique approaches and solutions for decentralised identity, contributing to the ongoing evolution of the digital identity landscape.
Final Thoughts
Decentralised identity offers promising potential for enhancing data privacy and identity verification, placing control and security back into the hands of individuals. As the concept of Self-Sovereign Identity continues to evolve, it opens up new opportunities for privacy-preserving digital interactions. Although challenges remain, the role of blockchain technology is becoming increasingly important in providing secure and private identity verification solutions. The importance of these systems will only grow more apparent as the adoption of the technology increases.