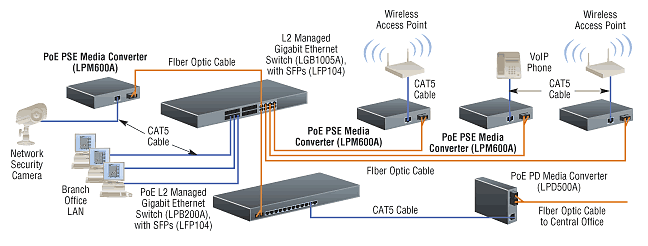
Introduction to Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a networking standard that enables networked devices to receive power via Ethernet cables. PoE-enabled devices can be powered by either an external power source or by an Ethernet connection.
PoE is commonly used to power IP phones, wireless access points, and other networked devices that require a small amount of power. It is also used in some industrial applications where devices need to be powered remotely.
There are two main types of PoE: active PoE and passive PoE. Active PoE injects power into the Ethernet cable, while passive PoE relies on the existing voltage in the cable to power the device. Active PoE is more commonly used than passive PoE because it is more reliable and provides more power to the device.
The most common type of active PoE is 802.3af, which can provide up to 15 watts of power to the device. 802.3at, also known as PoE+ or High Power over Ethernet (HPoE), can provide up to 30 watts of power. There are also newer standards, such as 802.3bt, which can provide up to 90 watts of power.
When choosing a Power over Ethernet standard, it is important to consider the wattage requirements of the devices that will be powered by it. The higher the wattage requirements, the higher the cost of the PoE system. However, higher wattage standards are becoming more common as devices
Types of Power over Ethernet
PoE comes in two main types: Passive and Active. With Passive PoE, the power is sent over the Ethernet cable along with the data. The device receiving the power extracts it from the cable. No negotiation takes place between the injector and receiver, so this method is typically used with devices that only support PoE, such as IP cameras. For more about Ethernet https://consolidatetimes.com/
With Active PoE, on the other hand, power is injected onto the Ethernet cable using an active device, such as a switch. The receiving device can then negotiate with the active device to determine how much power to draw from the cable. This method is often used with devices that can support both PoE and non-PoE modes, such as laptops and printers.
The Benefits of Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet, or PoE, is a technology that allows electrical power to be transmitted over standard Ethernet cable. This means that devices that require power, such as VoIP phones and wireless access points, can be powered using the same cable that carries their data signal.
PoE is a convenient and cost-effective solution for powering devices in difficult or remote locations, as it eliminates the need for extra power cables and outlets. It also reduces installation time and costs by allowing Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) to be installed near existing networking equipment.
In addition to its convenience, PoE also offers several other benefits:
Improved Reliability: By eliminating the need for external power supplies and AC/DC converters, PoE reduces the number of potential failure points in a system. This increases reliability and uptime for critical applications.
Reduced Power Consumption: PoE-powered devices consume less energy than those powered by AC/DC adapters or batteries, resulting in lower power bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Enhanced Security: Powering devices over Ethernet cable helps to prevent tampering and unauthorized access, as the electricity supply can be turned off at the network switch. This is valuable for security-sensitive applications such as video surveillance cameras.
Future Proofing: The latest generation of PoE standards (802.3bt) provides up to 100 watts of power per port, enough to power even the most demanding devices. This future-proofs your
Which Devices Use Power over Ethernet?
Power over Ethernet, or PoE, is a technology for wired Ethernet networks that allows network devices to be powered by the data cable instead of a separate power cable. This can simplify installation and reduce cabling costs.
PoE standards are defined by the IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at committees. The 802.3af standard provides up to 15 watts of power per port, while 802.3at increases this to 30 watts. Newer versions of the 802.3at standard, known as PoE+, provide up to 60 watts of power per port.
Devices that can be powered by PoE include IP phones, wireless access points, security cameras, and LED lights. In order for a device to use PoE, it must have a built-in PoE controller or be connected to one via an external adapter.
Conclusion
Thanks for reading our complete guide to Power over Ethernet standards. We hope you now have a better understanding of the different types of PoE standards and how they can be used in your business or home network. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to answer them.